How KTern.AI detects critical path in a project and what are the factors involved in the critical path?
What is critical task and why it requires importance in the project?
Manage your critical path
What does the critical path show about your project?

- The top sequence of tasks has no slack (also called "float") and therefore drives the finish date of the project. All tasks in this sequence are on the
- critical path and are called critical tasks. In the Detail Gantt view, critical tasks appear in red.
- The lower sequence of tasks does not drive the finish date of the project, and therefore the tasks are not critical. In the Detail Gantt view, noncritical tasks appear in blue.
- Total slack (or float) is the amount of time this sequence of tasks can slip before it affects the finish date of the project. In the Detail Gantt view, total slack appears as a thin teal line.
Scheduling Factors involved in formulation of critical path
| Factors involved | Description | Example |
| Predecessor Tasks | If you link your tasks, the predecessor tasks will be displayed in the Gannt Chart with their constraint types and the amount of lag time or lead time built in. | Two of the tasks in your project plan are Test and Release. You set up your project plan to reflect that the Release task begins 5 days after the Test task is completed, to allow for some time to watch for anomalies in the product before releasing it to customers. When you review the Gantt Chart for the Release task, you see the link to the Test task, with a Finish To Start constraint and a lag time of 5 days. |
Manually Scheduled or Auto Scheduled | If you have enabled the auto-scheduled the task then the dates will be automatically calculated based on the dependencies, constraint type and duration. If you have disabled the auto-scheduled task then dates will have to be entered manually. | if Task B depends on Task A, and Task A is set to finish on February 1st, with auto-scheduling enabled, Task B will automatically start on February 2nd and finish 5 days later, on February 6th, based on the 5-day duration. However, if auto-scheduling is disabled, you'd need to manually set Task B’s start date as February 2nd and input its end date as February 6th. |
Total Slack | If the total slack is always zero. This is because any delay in tasks on the critical path will directly impact the project’s finish date. For non-critical tasks, Total Slack can be positive, indicating that they can be delayed by a certain amount without affecting the critical path. | Let’s say the project needs to be finished by February 10th. If Task A starts on February 1st and ends on February 4th, Task B will start on February 5th and finish on February 10th. Task C will start on February 11th and finish on February 13th. If Task C is delayed by a couple of days, it won’t affect the project deadline because it has some slack time. However, if Task A or Task B is delayed, the entire project will be delayed, since they are on the critical path, meaning Total Slack for those tasks is zero. Task C has slack because it can be delayed without affecting the finish date. |
Business Scenario
| Task | Predecessor | Duration(in days) |
| A: Identification of Resources | -- | 5 |
| B: Requirement Gathering | -- | 7 |
| C: Resource Allotment for the Workstream | A | 9 |
| D: Business Workshops | A,B | 6 |
| E: Requirement Signoffs | D | 7 |
| F: Development Setup | C,E | 4 |
| G: Internal Workshop Meeting | E | 5 |
Let's now determine the critical path. There are four steps in the critical path analysis.
Build the project network.
Calculate the early start, early finish, late start, and late finish dates in the project.
Determine the project completion time.
- Identify the critical path and and calculate slack.
Critical Path Analysis
Step 1: Derive the network model
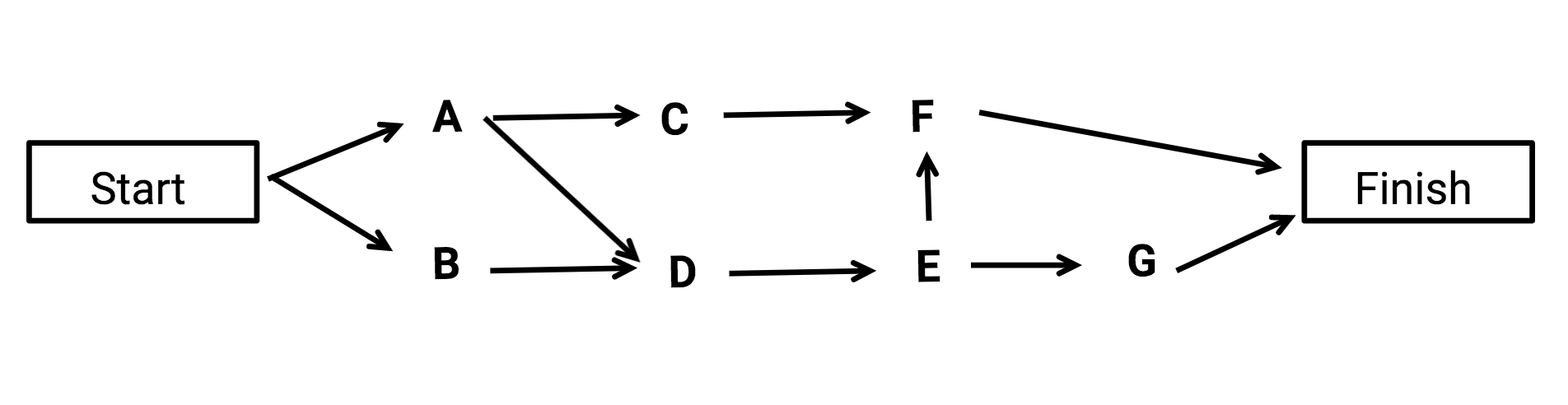
Let's draw the network path based on the given inputs. Activities A and B have no predecessors so they can begin at the start. C needs A to be completed before it can start. D should complete before E starts and C and E should finish before F. G depends on E. Since F and G have no successors they go to finish.
Before proceeding to the next step click here to understand the terms used in them.
Step 2: Forward Pass
Let's do the forward pass and calculate the early start, early finish, and late start, late finish dates.
ES of successor= Maximum (EF of all predecessors)
LF of predecessor = Minimum (LS of all the successors)
Slack= LS - ES or LF - EF

Forward Pass
A has no predecessor so its earliest start time will be 0. Since it has 5 days to finish , it's earliest finish time will be 0 + 5 which is 5 days.
B also can start at 0 and duration is 7 days, it will have an earliest finish time of 7.
Since the earliest finish time for A is 5, the earliest time C can start is 5 and with a task duration of 9 days, C will have the earliest finish time of 9 + 5= 14 days.
Since the earliest finish time for A and B are 5 and 7 respectively, and D needs both of them to finish in order to start, then the earliest time D can start is 7 i.e. the highest of the earliest finish times preceding a task will be the task’s earliest start time.
E here has only one predecessor D and can start on day 13 and finish earliest on day 20.
F has predecessors, C and E. Since the higher earliest finish time is 24 days, F can start earliest on day 20 and finish on day 24.
G can also start earliest on days 20 since it has only one predecessor and G can finish earliest days at 20 + 5 which gives 25 days.
- Note that G gives the highest earliest finish of 25 days. In essence, the project’s completion time is the highest earliest finish time at the finish node.
Backward Pass
At the finish node F and G has to be 25 i.e. F and G cannot take more than 25 days. Latest start times are obtained by subtracting the duration from the latest finish.
For G, the latest start time will be 25 - 5= 20 days. For F, the latest start will be 25-4= 21.
E has two successors F and G. As a result, the latest time E has to finish is 20 days in order for G to start. In essence, when doing a backward pass, the latest finish time of a task must be the minimum of the latest start times of its successors. Thus the latest start time for E will be 20 - 7 = 13 days.
D has only one successor E, so the latest finish time for D will be the latest start time for E which is 13 days. And, LS will be 13 - 6 = 7 days.
C also has one successor F. Therefore the latest finish will be 21 days for C and latest start will be 12 days.
A has two successors, C and D. The minimum of their latest start is 7 days. So the latest finish for A will be 7 days and its latest start will be 2 days.
B has one successor D with the latest start of 7 days. So the latest finish for B will be 7 days and its latest start will be 0.
Next step is to calculate the slack value. It can be done in two ways. Either by calculating the difference between the latest start and earliest start time ( LS - ES) or difference between the latest finish and earliest finish time ( LF - EF). Slack for A is 2 - 0 or 7 - 5 = 2 days. For B, slack is 0. For C the slack is 7 days. The slack values for D, E, and G are 0.
- In our scenario, the activity C can begin anytime between 5 and 12 days and it can finish anytime between 14 and 21 days. Thus C can be delayed for up to 7 days and the project will still be completed in 25 days. On the other hand tasks B, D, E and G cannot be delayed without extending the project’s completion time. For instance, if D is delayed by 2 days then the project completion time will be extended by 2 days, from 25 to 27 days. Thus, these sequence of tasks with zero slack are called critical tasks. The critical tasks must be completed on time in order for the project to meet its scheduled deadline. Critical path forms the longest path in the network. The critical path is B-D-E-G.
Key Takeaways:
- The critical path is the longest path in the network and determines project duration.
- Any delay in B, D, E, or G will extend the project’s completion date beyond 25 days.
- Tasks like A & C have slack, meaning they can be delayed without impacting the overall timeline.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing the critical path ensures that projects finish on time. By closely monitoring critical tasks, tracking dependencies, and managing slack, project managers can proactively address risks and ensure smooth project execution.
Related Articles
How Critical Path can be managed effectively In KTern.AI?
Understanding the Critical Path The critical path in your project is a sequence of tasks that directly or indirectly affects the project completion date. Before understanding critical path, let's understand dependency management in KTern.AI - ...How to Frame a Critical Path and Identify Tasks Under It in KTern?
Critical Path The Critical Path is the longest sequence of dependent tasks that determines the shortest possible duration for completing a project. It highlights the essential tasks that directly impact the project’s finish date. Any delay in a ...How To Manage Dependencies And Critical Path In KTern?
Effective project management often requires detailed tracking of task dependencies and the identification of critical paths. KTern offers robust tools to manage these aspects seamlessly. This documentation focuses on handling dependencies and ...How to Effectively Govern Overdue Tasks in KTern.AI?
Managing overdue tasks is crucial for maintaining project timelines, ensuring resource efficiency, and delivering high-quality outcomes. It prevents delays from cascading into larger issues, keeping projects on track and stakeholders satisfied. ...How baseline version and metrics are calculated in KTern.AI - Project Planner ?
Project Governance When managing projects, a "baseline" refers to the initial plan approved by key stakeholders, capturing expectations for scope, time, and cost. Tracking baseline metrics such as Baseline Start, Baseline End Date, Baseline Duration, ...